What is a Medical Endoscope ?
Instruction:
Medical endoscopy has revolutionized the field of diagnostic and therapeutic medicine. Endoscopes, the tools used in this practice, allow healthcare professionals to view and treat areas inside the body with minimal invasiveness. This guide will delve into what medical endoscopes are, their types, uses, and benefits.
Understanding Medical Endoscopes:
A medical endoscope is a flexible or rigid tube equipped with a light source and a camera. It is used to examine the interior of a body cavity or organ. Endoscopes transmit real-time images to a monitor, enabling doctors to see areas that are not visible with standard imaging techniques.
Components of an Endoscope:
Endoscopes consist of several key components that make them effective for medical procedures:
Light Source: Provides illumination inside the body.
Lens System: Captures and transmits images.
Control Section: Allows the operator to maneuver the endoscope and control its functions.
-Flexible or Rigid Tube: Houses the light source and lens system, and can bend to navigate through the body.
Types of Medical Endoscopes :
There are various types of endoscopes designed for specific medical applications. These can be broadly categorized into flexible and rigid endoscopes.
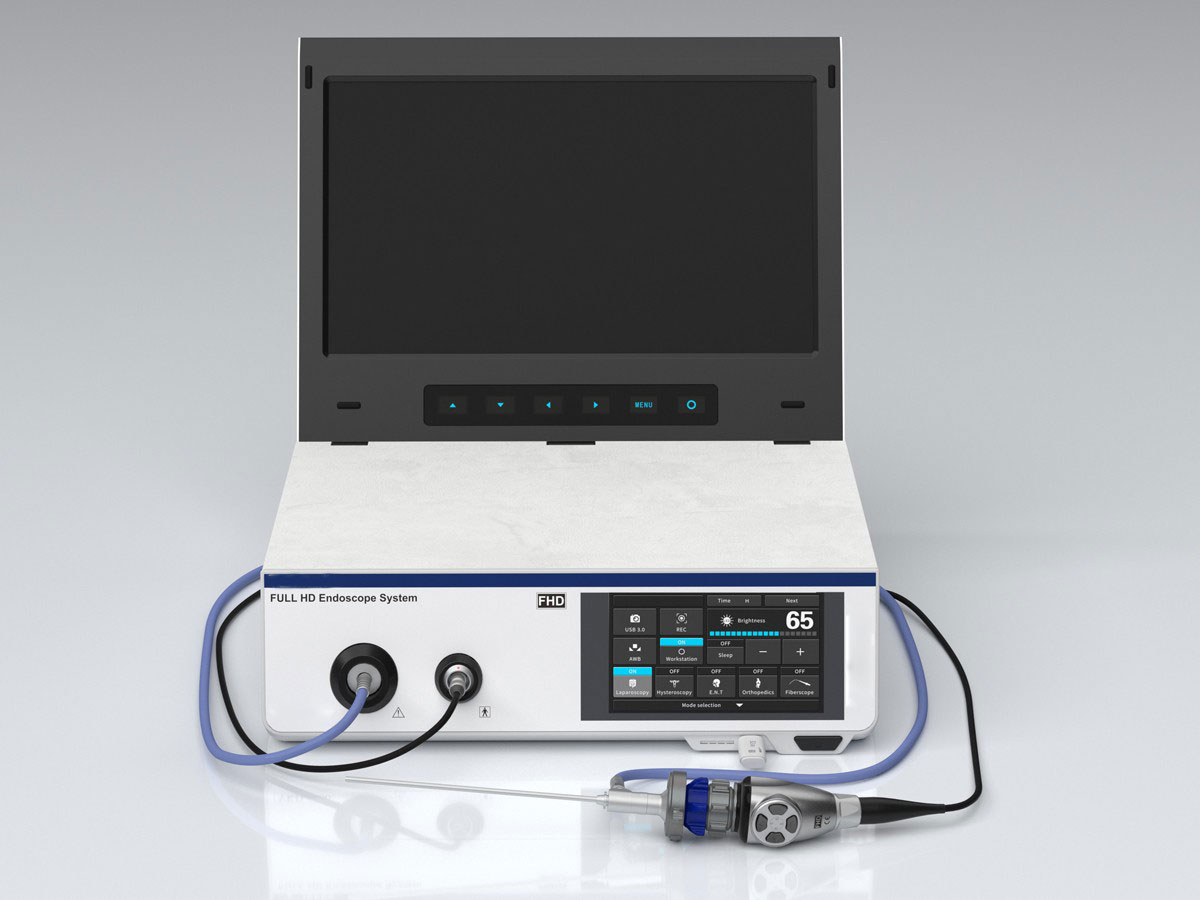
Flexible Endoscopes
Flexible endoscopes are bendable, making them ideal for navigating through winding and narrow pathways within the body. They are commonly used in:
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Examines the digestive tract using gastroscopes or colonoscopes.
Bronchoscopy: Looks at the airways and lungs.
Urethroscopy: Inspects the urinary tract.
Rigid Endoscopes
Rigid endoscopes are straight and are used for examining areas that do not require much maneuvering. They are typically employed in:
Arthroscopy: Inspects joints like the knee or shoulder.
Laparoscopy: Used in abdominal surgeries.
Cystoscopy: Examines the bladder.
Uses of Medical Endoscopes
Medical endoscopes have a wide range of diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Their minimally invasive nature makes them preferable for many procedures.
Diagnostic Uses
Endoscopes are invaluable in diagnosing various conditions, allowing doctors to:
Detect Diseases Identify abnormalities such as tumors, ulcers, and infections.
Biopsies: Collect tissue samples for further analysis.
Monitor Conditions: Track the progress of diseases and the effectiveness of treatments.
Therapeutic Uses
Beyond diagnostics, endoscopes are also used in treatments, including:
Surgery: Perform minimally invasive surgeries, reducing recovery time and risk.
Polyp Removal: Extract polyps from the colon.
Stone Removal: Remove stones from the kidney or gallbladder.
Benefits of Medical Endoscopy
The use of medical endoscopes offers numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare providers.
For Patients
Minimally Invasive: Endoscopic procedures require smaller incisions, leading to less pain and quicker recovery.
Reduced Risk: Lower risk of infection and complications compared to traditional surgery.
Shorter Hospital Stays: Many endoscopic procedures are outpatient, allowing patients to return home the same day.
For Healthcare Providers
Enhanced Visualization: Provides clear and magnified views of internal structures.
Precision: Allows for accurate diagnostics and targeted treatments.
Versatility: Can be used in various medical fields and procedures.
Conclusion
Medical endoscopes have become an integral part of modern medicine, offering a blend of diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities. Their ability to provide detailed internal views with minimal invasiveness has transformed patient care, making procedures safer and more efficient. As technology continues to advance, the role of endoscopes in medicine is likely to expand, further enhancing their benefits for both patients and healthcare professionals.

Leave A Comment